|
OpenFCST: The open-source Fuel Cell Simulation Toolbox
|
|
OpenFCST: The open-source Fuel Cell Simulation Toolbox
|
Base class for applications. More...
#include <application_base.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| ApplicationBase (boost::shared_ptr< ApplicationData > ex_data=boost::shared_ptr< ApplicationData >()) | |
| Constructor for an application. | |
| ApplicationBase (const ApplicationBase &other) | |
| Copy constructor. | |
| virtual | ~ApplicationBase () |
| Virtual destructor. | |
| virtual void | declare_parameters (ParameterHandler ¶m)=0 |
| Declare parameters for a parameter file. | |
| void | print_parameters_to_file (ParameterHandler ¶m, const std::string &file_name, const ParameterHandler::OutputStyle &style) |
| Print default parameters for the application to a file. | |
| virtual void | initialize (ParameterHandler ¶m)=0 |
| Pure virtual initialization function. | |
| virtual void | remesh () |
| Generates the next mesh depending on the mesh generation parameters. | |
| virtual void | init_vector (FEVector &dst) const |
| Initialize vector to problem size. | |
| virtual void | start_vector (FEVector &dst, std::string caller) const |
| Initialize vector to problem size. | |
| virtual double | residual (FEVector &dst, const FEVectors &src, bool apply_boundaries=true) |
Compute residual of src and store it into dst. | |
| virtual void | solve (FEVector &start, const FEVectors &rhs) |
Solve the system assembled with right hand side rhs and return the result in start. | |
| virtual void | Tsolve (FEVector &start, const FEVectors &rhs) |
Solve the dual system assembled with right hand side rhs and return the result in start. | |
| virtual double | estimate (const FEVectors &src) |
| Error estimation. | |
| virtual double | evaluate (const FEVectors &src) |
| Evaluate whatever the simulation was made for. | |
| virtual void | grid_out (const std::string &filename) const |
| Write the mesh in the format specified by the ParameterHandler. | |
| virtual void | data_out (const std::string &filename, const FEVectors &src) |
| Write data in the format specified by the ParameterHandler. | |
| virtual void | data_out (const std::string &filename, const FEVectors &src, const std::vector< std::string >) |
| boost::shared_ptr < ApplicationData > | get_data () |
| Get access to the protected variable data. | |
| const boost::shared_ptr < ApplicationData > | get_data () const |
| Get read-only access to the protected variable data. | |
| virtual std::string | id () const |
| Return a unique identification string for this application. | |
| virtual void | notify (const Event &reason) |
| Add a reason for assembling. | |
| virtual void | clear () |
| Reset the application class such that a call to initialize() is possible again and will produce the same result as if the object was fresh. | |
| void | clear_events () |
| Clear all notifications. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | print_caller_name (const std::string &caller_name) const |
| Print caller name. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| boost::shared_ptr < ApplicationData > | data |
| Object for auxiliary data. | |
| Event | notifications |
| Accumulate reasons for reassembling here. | |
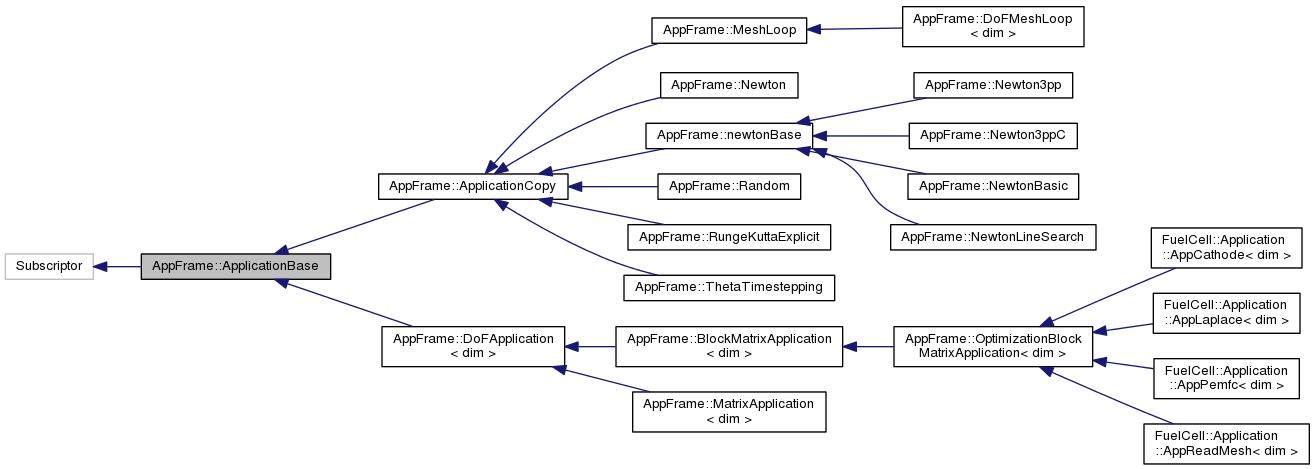
Base class for applications.
get_application()
The idea of these application classes is the possibility to build a chain out of these in order to have several predefined nested solvers. For this, we distinguish applications roughly in two classes, both derived from ApplicationBase:
Terminal applications, which implement the real finite element code like computing residuals on mesh cells, assembling matrices and solving linear systems.
Usually an class in a chain communicates values with its next outer class through function arguments. Nevertheless, at least the terminal application will require values from even outer applications in the chain in order to compute residuals and matrices correctly. For these, the mechanism of named data provided by ApplicationData was introduced. Each class can store auxiliary data under a unique name there for use in inner iterations.
|
inline |
Constructor for an application.
One task of the constructor is declaring parameters for an application. Since this is done consecutively for derived classes, all parameters may be declared in a modular way. Derived classes should create unique subsections in the ParameterHandler.
References AppFrame::Event::all(), data, and notifications.
|
inline |
Copy constructor.
Generate a new application sharing the same ApplicationData with another one.
References AppFrame::Event::all(), and notifications.
|
inlinevirtual |
Virtual destructor.
|
inlinevirtual |
Reset the application class such that a call to initialize() is possible again and will produce the same result as if the object was fresh.
|
inline |
Clear all notifications.
|
inlinevirtual |
Write data in the format specified by the ParameterHandler.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppPemfc< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppCathode< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppReadMesh< dim >, AppFrame::DoFMeshLoop< dim >, AppFrame::ApplicationCopy, and AppFrame::MeshLoop.
References print_caller_name().
|
inlinevirtual |
|
pure virtual |
Declare parameters for a parameter file.
Pure virtual function MUST be redeclared in derived classes.
Implemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppCathode< dim >, AppFrame::MatrixApplication< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppPemfc< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppReadMesh< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppLaplace< dim >, AppFrame::OptimizationBlockMatrixApplication< dim >, AppFrame::DoFMeshLoop< dim >, AppFrame::BlockMatrixApplication< dim >, AppFrame::ThetaTimestepping, AppFrame::newtonBase, AppFrame::Newton, AppFrame::Random, AppFrame::MeshLoop, AppFrame::NewtonBasic, AppFrame::NewtonLineSearch, AppFrame::RungeKuttaExplicit, and AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
|
inlinevirtual |
Error estimation.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppCathode< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppPemfc< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppLaplace< dim >, and AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
References print_caller_name().
|
inlinevirtual |
Evaluate whatever the simulation was made for.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppPemfc< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppLaplace< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppCathode< dim >, and AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
References print_caller_name().
|
inline |
Get access to the protected variable data.
|
inline |
Get read-only access to the protected variable data.
|
inlinevirtual |
Write the mesh in the format specified by the ParameterHandler.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
References print_caller_name().
|
inlinevirtual |
Return a unique identification string for this application.
In particular, it returns the name of the class in which the object you requested id() from belongs to. For example: cBase* a = new cBase cBase* b = new cDerived then, a->id() will return cBase and b->id() will return cDerived
Reimplemented in AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
|
inlinevirtual |
Initialize vector to problem size.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >, and AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
References print_caller_name().
Referenced by start_vector().
|
pure virtual |
Pure virtual initialization function.
Here, the parameters declared in the constructor are actually read from ParameterHandler.
This function must be overloaded in any derived class using its own values from the parameter file.
Initialization functions of derived classes must make sure to call all functions _initialize() of the base classes.
Implemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppCathode< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppPemfc< dim >, AppFrame::MatrixApplication< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppLaplace< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppReadMesh< dim >, AppFrame::OptimizationBlockMatrixApplication< dim >, AppFrame::DoFMeshLoop< dim >, AppFrame::BlockMatrixApplication< dim >, AppFrame::ThetaTimestepping, AppFrame::newtonBase, AppFrame::Newton, AppFrame::Random, AppFrame::MeshLoop, AppFrame::NewtonBasic, AppFrame::NewtonLineSearch, AppFrame::ApplicationCopy, and AppFrame::RungeKuttaExplicit.
|
inlinevirtual |
Add a reason for assembling.
The new reason is binary or'd with the previous ones.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
|
inlineprotected |
Print caller name.
Referenced by data_out(), estimate(), evaluate(), grid_out(), init_vector(), remesh(), residual(), solve(), start_vector(), and Tsolve().
|
inline |
Print default parameters for the application to a file.
Note that this member function MUST be called after declare_parameters. For example:
|
inlinevirtual |
Generates the next mesh depending on the mesh generation parameters.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >, AppFrame::MatrixApplication< dim >, AppFrame::BlockMatrixApplication< dim >, and AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
References print_caller_name().
|
inlinevirtual |
Compute residual of src and store it into dst.
The bool variable is used to specify if boundary conditions should be applied using FilteredMatrix.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::DoFApplication< dim >.
References print_caller_name().
Solve the system assembled with right hand side rhs and return the result in start.
Reimplemented in FuelCell::Application::AppCathode< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppPemfc< dim >, FuelCell::Application::AppLaplace< dim >, AppFrame::ThetaTimestepping, AppFrame::Random, AppFrame::Newton, AppFrame::NewtonBasic, AppFrame::newtonBase, AppFrame::MeshLoop, AppFrame::NewtonLineSearch, AppFrame::ApplicationCopy, AppFrame::RungeKuttaExplicit, AppFrame::Newton3pp, and AppFrame::Newton3ppC.
References print_caller_name().
|
inlinevirtual |
Initialize vector to problem size.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
References init_vector(), and print_caller_name().

Solve the dual system assembled with right hand side rhs and return the result in start.
Reimplemented in AppFrame::ApplicationCopy.
References print_caller_name().
|
protected |
Object for auxiliary data.
This object is always valid, since it is either handed to the constructor or created there.
Referenced by ApplicationBase().
|
protected |
Accumulate reasons for reassembling here.
If any of those is set, the function solve() of a terminal application must take care of reassembling the matrix.
Referenced by ApplicationBase().
 1.8.2
1.8.2